IT security for health data
According to a study conducted by Intertrust, 71% of medical applications have at least one major security vulnerability.
One of the CNIL’s recommendations concerns IT optimization such as use of complex passwords or data encryption. Naturally, the information systems of healthcare facilities must be protected and monitored regularly.
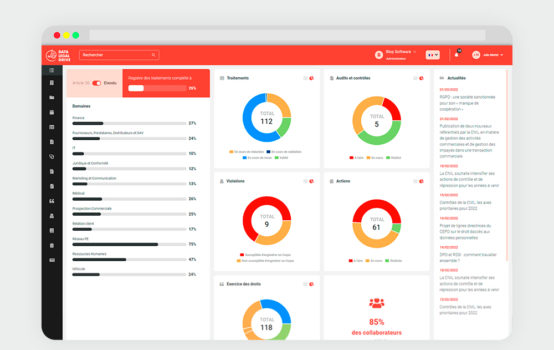
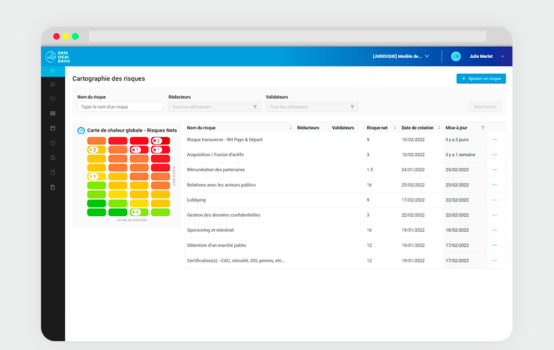
To limit the risk of a cyberattack, a mapping of existing risks and cyber threats for the healthcare facility must be compiled. To do this, the medical entity must map their processing activities beforehand, listing all personal data collected. This requirement is facilitated with GDPR software such as Data Legal Drive, which is designed to simplify the compliance programs of medical entities.
All concerned agents and healthcare personnel must be made aware of the issues tied to health data protection through training and e-learning programs.
If necessary, a task force involving management, the IT division, the legal division and the DPO must be set up.
In 2021, two physicians were sanctioned for security reasons: thousands of medical images hosted on servers belonging to the physicians were freely available to anyone on the internet. The reasons for this security breach? An incorrect configuration of the router and lack of systematic encryption.