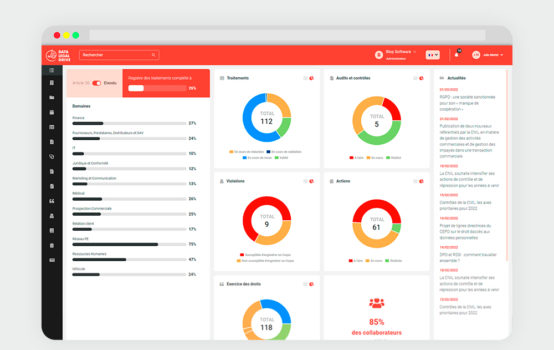
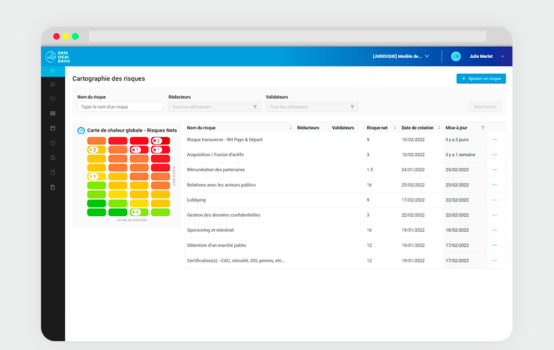
Local government: why the need to be GDPR-compliant?
Among public organizations, local government is under the strongest scrutiny.
Local governments collect and manage thousands of items of personal data, whether from citizens, constituents, or local elected officials.
Facial recognition, videosurveillance, etc. Though regional actors use collected data to make political decisions, municipalities are also facing the issues resulting from innovation and the acceleration of new technologies. They must intensify their efforts to protect personal data usage for digital and local projects.
Big data, cities of the future, connected cities, etc. With the enthusiasm surrounding smart cities, the data collected is used by local government to understand the behavior and usages of their towns’ inhabitants. At the same time, cities and urban agglomerations seeking to become smart cities must be aware of the challenges tied to the collection of various types of data, some of which is personal data.
While some cities are testing electronic voting system, others are simply launching or improving their websites to allow citizens to perform administrative formalities such as requests for civil status certificates, voter registration or other administrative documents.
Regardless of the town’s, agglomeration’s or department’s political strategy, personal data is diverse and growing in volume. GDPR is firstly a law to be observed, but local government should view GDPR compliance as a civic duty.